Number: Singular, Dual, Plural Noun in Arabic
Table of Content [View]
As you know, there are three parts of speech in Arabic, they are noun, verb, and particle. I'm still writing about the first point from parts of speech, noun.
I recommend you read the previous theory about noun in Arabic, so that you will gain more complete understanding.
Below are the subject (If you haven't read them before, just click the link for reading):
1. Parts of speech in Arabic
2. Definite noun & indefinite noun in Arabic
3. Noun cases in Arabic: nominative, accusative, genitive
4. Noun gender: masculine noun & feminine noun
Returning to the main subject at hand: ma'dud, which includes singular noun, dual noun, and plural noun.
The grammatical differences between English and Arabic
English nouns have singular and plural forms, while Arabic includes singular, dual, and plural as follows:- Singular (الْمُفْرَدُ)
- Dual (الْمُثَنَّى)
- Plural (الْجَمْعُ)
Number in Arabic: Singular, Dual, Plural
In the Arabic language, nouns have different forms depending on whether they are singular, dual, or plural.
Dual noun
Dual is used to refer to two things of the same kind, for example, two pens, two boys, two books, etc.
How do you form a dual noun from a singular noun?
The dual is formed by replacing the case ending of the singular form with the following:
1. Masculine noun.
a. For nominative case.
Add the suffixes with انِ (aani).
Examples:
Singular form = كِتَابٌ
Dual form = كِتَابَانِ
b. For accusative and genitive case
Add the suffixes with يْنِ (ayni)
Examples:
Singular form = كِتَابٌ
Dual form = كِتَابَيْنِ
2. Feminine noun
a. For nominative case
A singular female noun's final ta marbutah (ة) becomes regular ta (ت).
Add the suffixes with انِ (aani).
Examples:
Singular form = مُسْلِمَةٌ
Dual form = مُسْلِمَتَانِ
b. For accusative and genitive case
The final ta marbutah (ة) in a singular female noun becomes regular ta (ت).
Add the suffixes with يْنِ (ayni)
Examples:
Singular form = مُسْلِمَةٌ
Dual form = مُسْلِمَتَيْنِ
=====================================
Do you want to know about noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive) or you want to restudy this subject, just click here: noun cases in Arabic.
=====================================
If you have read the lesson about lists of feminine nouns, you must know that some feminine nouns end with اءُ and ى.
In this lesson, I will show you how to form dual nouns for a feminine noun which ends with اءُ and ى
a. When a singular feminine noun ends with اءُ, the final hamzah is replaced by و, for example:
Singular form = حَمْرَاءُ (red)
Dual for nominative case = حَمْرَاوَانِ
Dual for accusative and genitive case = حَمْرَاوَيْنِ
b. the final ى of singular noun becomes ي
Examples:
singular form = مُسْتَشْفَى = a hospital
Dual form for nominative case = مُسْتَشْفَيَانِ
Dual form for accusative and genitive case = مُسْتَشْفَيَيْنِ
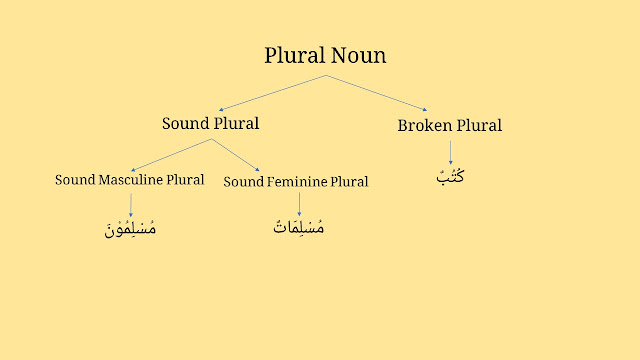
Plural noun
There are two types of plural in Arabic, they are sound plural and broken plural.
1. Sound plural / الْجَمْعُ السَّالِمُ
Sound plural (al-jam'u al-salim) means the original form (singular form) of the noun doesn't change.
a. the sound masculine plural / جَمْعُ المُذَكَّرِ السَّالِمِ
Example:
Singular form = مُسْلِمٌ
Plural form for nominative case = مُسْلِمُوْنَ
Plural form for accusative and genitive case = مُسْلِمِيْنَ
b. the sound feminine plural / جَمْعُ المُؤَنَّثِ السَّالِمِ
Example:
Singular form = مُسْلِمَةٌ
Plural form for nominative case = مُسْلِمَاتٌ
Plural form for accusative and genitive case = مُسْلِمَاتٍ
2. Broken plural / الْجَمْعُ الْمُكَسَّرُ
A lot of nouns have a plural form called the broken plural. In Arabic, we call it جَمْعُ التَّكْسِيْرِ
In English, we've known about irregular plurals, such as man (singular)-men(plural), foot (singular)-feet (plural), etc.
In English, we've known about irregular plurals, such as man (singular)-men(plural), foot (singular)-feet (plural), etc.
In Arabic, the plural form of a noun is created by making changes to the noun's singular form, using various patterns that involve deletions, prefixes, and suffixes.
I will show you the patterns in the next article.
In this article, I want to introduce to you the concept of broken plurals and provide some examples.
Note:
Some singular nouns may have more than one form of broken plural, and some may have both a sound plural and a broken plural.
Recommendation:
It's advisable to learn both the singular and plural forms of nouns when studying vocabulary related to them.
In this article, I want to introduce to you the concept of broken plurals and provide some examples.
Note:
Some singular nouns may have more than one form of broken plural, and some may have both a sound plural and a broken plural.
Recommendation:
It's advisable to learn both the singular and plural forms of nouns when studying vocabulary related to them.
==*Recommended reading*==
Enrich your Arabic vocabulary by memorizing these vocabularies:
Recommended e-book: Singular and plural nouns in Arabic
==*Recommended reading*==
Examples of broken plurals
- بَيْتٌ ( a house) - بُيُوْتٌ (houses)
- كِتَابٌ ( a book) - كُتُبٌ (books)
- كَبِيْرٌ (big) - كِبَارٌ (big)
- وَلَدٌ (a boy) - أَوْلاَدٌ (boys)
- مَالٌ (a property) - أَمْوَالٌ (properties)
- رَجُلٌ ( man) - رِجَالٌ (men)
- شَهْرٌ (a month) - أَشْهُرُ / شُهُوْرٌ (months)
- قَلْبٌ (heart) - قُلُوْبٌ (hearts)
- جَبَلٌ (a mountain) - جِبَالٌ (mountains)
- قَلَمٌ (a pen) - أَقْلاَمٌ (pens)
I will continue on the next lesson , in shaa Allah.
=============================
Related article : ordinal number in Arabic





this really helped! thx.
ReplyDeletethis rlly gud!
ReplyDelete