Noun Gender in Arabic - masculine noun & feminine noun
Table of Content [View]
We have already learned characteristics of noun in Arabic
In the article, I explained you that noun can inflect according to following things:
1. State (definite and indefinite).
2. Number (singular, dual, plural)
3. Gender (masculine, feminine)
4. Cases (nominative, accusative, genitive).
I've showed you at the previous article : noun cases (point number 4) and noun state (point number 1).
Today, I'm going to explain you point number 3, masculine noun and feminine noun in Arabic.
Noun Gender in Arabic: Masculine and Feminine
There are two genders in Arabic, they are masculine / مُذَكَّر and feminine / مُؤّنَّث
In this article, I will show you some points that have to be remembered
Below are the points:
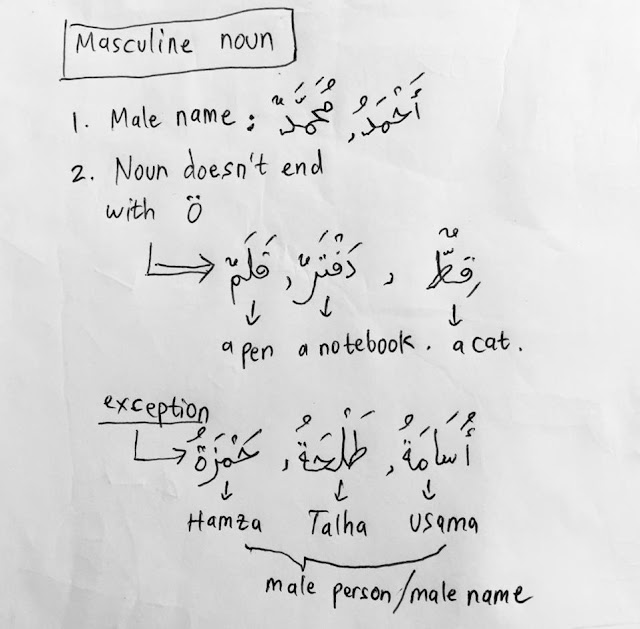
1. All nouns in Arabic are either masculine or feminine.
2. Masculine in Arabic is مُذَكَّر whereas feminine is مُؤّنَّث .
3. There are two kinds of nouns, they are: noun that refers to human beings, and noun that refer to non-numan.
4. The gender of human nouns follow the gender of the person.
Example:
أَحْمَدُ = masculine noun
آمِيْنَةُ = feminine noun
5. Feminine noun always ends in the symbol ة (ta marbuuta) / تاء مربوطة
There are some exceptions, and I will explain you later.
Examples:
سَاعَةٌ = a watch
سَيَّارَةٌ = a car
6. Most noun that refer to people can be made feminine by adding ة at the end of the masculine noun.
Examples:
a. teacher
a teacher (male) => مُدَرِّسٌ
a teacher (female) => مُدَرِّسَةٌ
b. Friend
a friend (male) => صَدِيْقٌ
a friend (female) => صَدِيْقَةٌ
7. Masculine noun never ends in the symbol ة (ta marbuuta) / تاء مربوطة
There are some exceptions, and I will explain you later.
Examples:
كِتَابٌ = a book
قَلَمٌ = a pen
8. Determiner is word placed before noun.
The function of determiner is to make it clear what the noun refers to.
Determiners have an agreement with noun, if noun is masculine, it's determiner is also masculine, and vice versa.
Example of determiners:
a. definite article : the / اَلْ
b. demonstratives: this, that, these, those.
c. Subject pronoun: he, she , I, etc
d. etc.
Sentence examples:
- This is a book => هَذَا كِتَابٌ
كِتَابٌ is masculine noun, therefore the demonstrative pronoun is also masculine (هَذَا )
- This is a car => هَذِهِ سَيَّارَةٌ
سَيَّارَةٌ is feminine noun, therefore the demonstrative is also feminine ( هَذِهِ )
You can read the previous lesson regarding demonstrative pronoun for complementing this subject:
- Demonstrative pronoun for near distance - masculine and singular noun
- Demonstrative pronoun for far distance - masculine and singular noun
- Demonstrative pronoun for far distance - feminine and singular noun
9. There is no neutral (non-gendered) pronoun (such as: "it" in English).
We must use either هُوَ (masculine pronoun) or هِيَ (feminine pronoun) depending on noun's gender.
10. The gender of adjectives, pronouns, and verbs that refers to noun must have an agreement with noun.
Examples:
a diligent man = رَجُلٌ مُجْتَحِدٌ
a diligent woman = إِمْرَأَةٌ مُجْتَحِدَةٌ
Lists of Feminine noun
1. Most parts of the body which occur in pairs are feminine.
Examples:
- eye = عَيْنٌ
- foot = رِجْلٌ
- hand = يَدٌ
2. Name of women (even their name don't end with ta marbuta / ة )
Example:
- مَرْيَمُ = Maryam
- زَيْنَبُ = Zainab
3. Nouns that are feminine by nature
Examples:
- أُخْتٌ = sister
- أُمٌّ = mother
- عَرُوْسٌ = bride
- حَامِلٌ = pregnant.
4. Geographical proper names, such as country, city, villages.
Examples:
- بَارِيْسُ = Paris
- مَدِيْنَةٌ = city
5. There are some nouns which can be either masculine or feminine.
Examples:
- قِدْرٌ = cooking pot.
- سُوْقٌ = market
- حَالٌ = condition
- سِكِّيْنٌ = knife
6. Nouns are feminine by usage
Examples:
- أَرْضٌ = earth
- شَمْسٌ = sun
7. Feminine endings
Beside ة (ta marbuta), there are also two other feminine endings, they are:
a. Words ending with اءُ
Examples:
- خَضْرَاءُ = green
- حَمْقَاءُ = stupid
b. words ending with ى
- كُبْرَى = bigger
- عَطْشَى = thirsty.
How do we identify a noun as a masculine noun or a feminine noun?
Below are the ways to differentiate the gender of noun:
1. If the noun is human/animal, we can determine the gender of noun whether it masculine or feminine by directly seeing the gender.
Examples:
الْمَرْأَةُ is human noun, it means the woman => feminine noun.
أَحْمَدُ is a man => masculine noun.
2. Feminine noun mostly ends with ة , the others are masculine noun.
Examples:
- مُدَرِّسَةُ = a female teacher.
- حَدِيْقَةُ = a garden
Exception:
There are some masculine nouns that have ending with ta marbuta ( ة ), for examples:
- حَمْزَةُ ends with ة , but this is the name of man => masculine noun.
- أُسَامَةُ ends with ة , but this is man's name => masculine noun.
3. Things in pairs are feminine noun, such as:
- parts of body in pairs, ex: يَدٌ
- things in pairs, ex: أَرْضٌ , شَمْسٌ , etc.
4. Feminine noun endings with اءُ and ى . See feminine endings point above.
Summary
Below are summary in a picture to simplify the masculine & feminine noun concept.
 |
| Masculine noun in Arabic |
 |
| Feminine noun in Arabic |
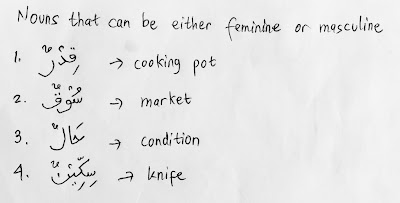 |
| Examples of noun that can be either feminine or masculine |

Good work on this topic ماشاءاللہ
ReplyDelete