Mudaf and Mudaf Ilaihi: Meaning, Rules, and Examples
Today, we are going to learn compound words in Arabic. The construction contains two nouns (or more than two), the first noun is called mudaf, and the second one is called mudaf ilaihi.
A Compound words which is called al-idaafah
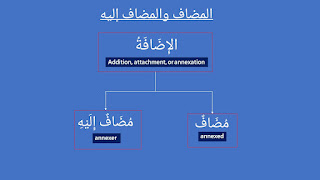
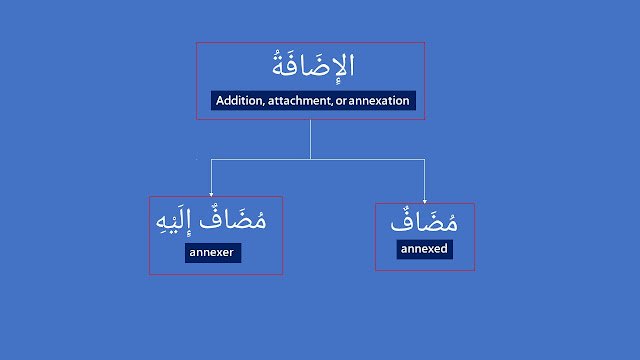
The compound in which both parts are nouns. The first noun is related to the second one. This relationship between these two nouns is called al-idafah (الإِضَافَةُ).
Mudaf - Mudaf ilaihi Meaning
The meaning of idaafah (إِضَافَةٌ) : addition, attachment, or annexation.
The first part of al-idaafah is called mudaaf (مُضَافٌ) while the second part is called mudaaf ilayhi (مُضَافٌ إِلَيْهِ).
The meaning of mudaaf (مُضَافٌ) : attached or annexed.
The meaning of mudaaf ilaihi (مُضَافٌ إِلَيْهِ) : attacher or annexer.
Al-idafah in Arabic vs compound noun in English
English construction
Al-idafah corresponds to the genitive construction and is similar to English "... of ..." or "...'s".
In English, you say, “name of the boy.” or “boy's name.”
Arabic construction
The name of the boy (the boy's name) in Arabic is اِسْمُ الوَلَدِ (ismu al-waladi).
Ismu (اِسْمُ) is annexed.
al-waladi (الوَلَدِ ) is annexer.
This one of Arabic construction (annexed-annexer) is called mudaf-mudaf ilaihi (المضاف والمضاف إليه).
Mudaf is attributed to the mudaf ilaihi.
المُضَافُ (al-mudaaf) in English is also called construct, whereas المُضَافُ إِلَيْهِ (al-mudaaf ilaihi) is also called genitive.
Mudaf mudaf ilaihi rules
1. Mudaf always precedes mudaf ilaihi.
2. Mudaf will never have alif lam (ال) or definite article or alif lam ma'rifah at the beginning. Mudaf has no tanwiin (تنوين) also.
3. The case of a mudaf can be dammah (marfu'), fat-hah (mansub), or kasrah (majrur), depending on what precedes it (according to the 'aamil governing it).
4. Mudaf ilaihi can be in ma'rifah form or nakirah (definite form or indefinite).
5. Mudaf ilaihi is in genitive case (always majruur).
The type of relationship between mudaf and mudaf ilaihi
1. Possessed and possessor
Example:
كِتَابُ مُحَمَّدٍ (kitaabu muhammadin), the meaning is Muhammad's book.
kitaabu is mudaf, whereas muhammadin is mudaf ilayhi.
كِتَابُ is acted as possessed
مُحَمَّدٍ is acted as possessor.
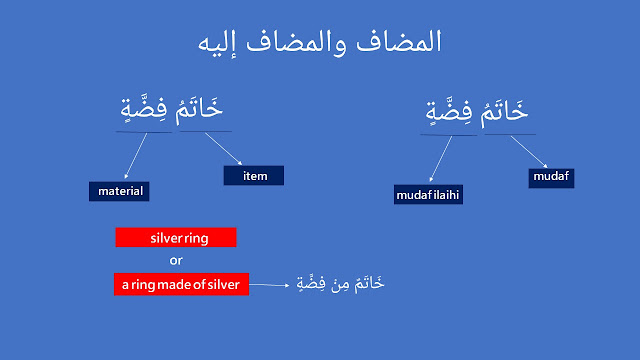
2. Mudaf is acted as type (جِنْسٌ) of the mudaf ilaihi (item and material)
Example:
خَاتَمُ فِضَّةٍ (khaatamu fiddatin), the meaning is silver ring.
khaatamu is mudaf, whereas fiddatin is mudaf ilaihi.
خَاتَمُ is acted as item.
فِضَّةٍ is acted as material.
Item "خَاتَمُ " is made of material "فِضَّةٍ ".
Note:
You can also use the preposition مِنْ (min) to express the material.
خَاتَمٌ مِنْ فِضَّةٍ = a ring made of silver.
Summary
خَاتَمُ فِضَّةٍ (khaatamu fiddatin) = خَاتَمٌ مِنْ فِضَّةٍ (khaatamun min fiddatin)
3. Mudaf ilaihi is acted as a zarf (ظرف)
Example:
صَلاَةُ اللَّيْلِ (salaatu al-layli), the meaning is night prayer.
salaatu is mudaf, whereas al-layli is mudaf ilaihi.
اللَّيْلِ is acted as zarf zaman (adverb of time).
The meaning is صَلاَةٌ فِي اللَّيْلِ (salaatun fii al-layli) = prayer at night.
Summary
صَلاَةُ اللَّيْلِ (salaatu al-layli) = صَلاَةٌ فِي اللَّيْلِ (salaatun fii al-layli)
4. Mudaf is acted as a part of the mudaf ilaihi
Example:
قِطْعَةُ خُبْزٍ (qit'atu khubzin), the meaning => a piece of bread
qit'atu is mudaf while khubzin is mudaf ilaihi.
قِطْعَةُ is part, whereas خُبْزٍ is whole.
The adjective of the mudaf
The rule if there is an adjective of the mudaf:
1. Mudaf precedes mudaf ilaihi.
2. There is no word can interpose between mudaf and mudaf ilaih.
3. The adjective of the mudaf has to be placed after the mudaf ilaih.
Example
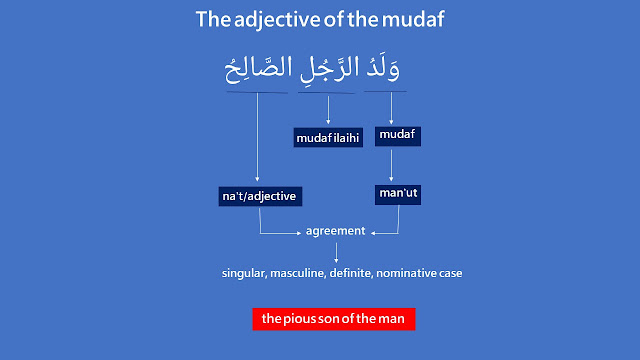
— the pious son of the man ⇒ وَلَدُ الرَّجُلِ الصَّالِحُ (waladu ar-rajuli as-saalihu).
The explanation of this construction
وَلَدُ (waladu) is mudaf. Because of mudaf, it has no tanwiin and no ال
الرَّجُلِ (ar-rajuli) is mudaf ilaihi. Therefore, it is in genitive case (majruur).
الصَّالِحُ (as-saalihu) is the adjective of the noun وَلَدُ (waladu).
Because وَلَدُ (waladu) is ma'rifah or definite, so the adjective is also definite, therefore we add ال to the word صالح
Additional note:
Because there is an agreement between noun and it's adjective in terms of number, gender, definiteness, and case, therefore the word saalih is singular, masculine, definite, and in nominative case (marfu').
وَلَدُ = singular, masculine, definite, nominative case (marfu').
الصَّالِحُ = singular, masculine, definite, nominative case (marfu').
The question
How do you translate the following text : وَلَدُ الرّجُلِ الصَّالِحِ (waladu ar-rajuli as-saalihi)?
The answer
First, you have to notice the word الصَّالِحِ
الصَّالِحِ = singular, masculine, definite, genitive (majruur).
Because as-saalihi is in genitive case (majruur), and the word ar-rajuli is in the same condition, so as-saalihi is an adjective of ar-rajuli.
Finally, the meaning is :The son of the pious man.
Summary
وَلَدُ الرَّجُلِ الصَّالِحُ (waladu ar-rajuli as-saalihu), the meaning is => the pious son of the man.
وَلَدُ الرّجُلِ الصَّالِحِ (waladu ar-rajuli as-saalihi), the meaning is => the son of the pious man.
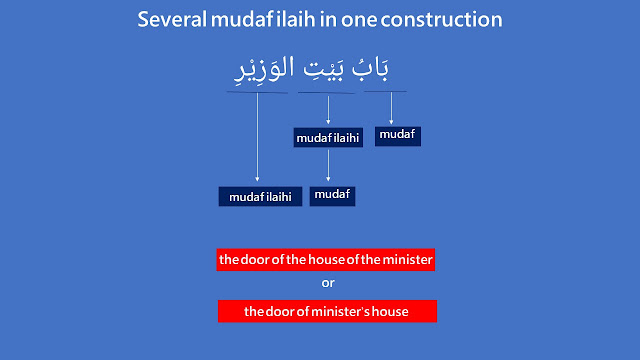
Several mudaf ilaih in one construction
Sometimes there are more than one mudaf ilayh in one construction, for examples:
— The door of the house of the minister (The door of the minister's house)
— The door of the house of the minister's son.
The rule if there are several mudaf ilaih in one construction: the middle mudaf ilaihi becomes mudaf of the succeeding words.
Therefore (أل) alif lam ma'rifah cannot precede it nor can tanwiin be appended to it.
Examples
Let's see the first example: the door of the house of the minister.
In Arabic, based on the rule above, you say, "بَابُ بَيْتِ الوَزِيْرِ" (baabu baiti al-waziiri).
Construction explanation
بَابُ (baabu) is mudaf.
بَيْتِ (bayti) is mudaf ilaihi. Therefore, it is in genitive case (majrur).
بَيْتِ (bayti) is also acted as mudaf. Therefore, it has no alif lam ma'rifah (definite article) and no tanwiin.
الوَزِيْرِ (al-waziiri) is mudaf ilaihi. Therefore, it is in genitive case.
Then, let's observe the second example: The door of the house of the minister's son.
The door of the house of the minister's son in Arabic => بَابُ بَيْتِ ابْنِ الوَزِيْرِ (baabu bayti bni al-waziiri).
The explanation of the construction
بَابُ (baabu) is mudaf. It has no tanwiin and no ال
بَيْتِ (bayti) is mudaf ilaihi. It is in genitive case (majruur) because mudaf ila baabu (genitive from baabu).
بَيْتِ (bayti) is also acted as mudaf. Because of this, it has no tanwiin and no ال
ابْنِ (ibni) is mudaf ilaihi. It is mudaf ila bayti (genitive from bayti). Therefore, it is in genitive case (majruur).
ابْنِ (ibni) is also acted as mudaf. Because of this reason, it has no ال and no tanwiin.
الوَزِيْرِ (al-waziiri) is mudaf ilaihi. It is mudaf ila ibni (genitive from ibni). So, it is in genitive case (majruur).
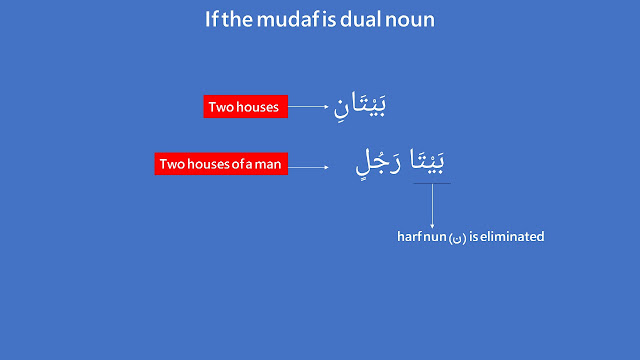
Ism muthanna (dual noun) and ism jam' mudhakkar salim (sound masculine plural noun) are acted as mudaf
The rule when dual and sound masculine plural noun are acted as mudaf is ⇒ the nun (نون) at the end is deleted.
Examples:
— two houses of a man = بَيْتَا رَجُلٍ (baytaa rajulin).
Two houses originally was بَيْتَانِ (baytaani). Because this word is in al-idaafah construction and acted as mudaf, so harf nun at the end is eliminated.
— boy's teachers (the teachers of the boy) = مُدَرِّسُو الوَلَدِ (mudarrisuu al-waladi).
Teachers originally was مُدَرِّسُونَ (mudarrisuuna). Because it is in al-idafah construction and acted as mudaf, so harf nuun is omitted.
Examples of mudaf and mudaf ilaihi in al-Quran
1. هَلْ أَتَىٰكَ حَدِيثُ ٱلْغَـٰشِيَةِ
(al-ghashiyah:1)
حَدِيثُ = mudaf
ٱلْغَـٰشِيَةِ = mudaf ilaih
2. ٱلْحَمْدُ لِلَّهِ رَبِّ ٱلْعَـٰلَمِينَ
(al-fatihah:2)
رَبِّ = mudaf
ٱلْعَـٰلَمِينَ = mudaf ilaih
3. قُلْ أَعُوذُ بِرَبِّ ٱلنَّاسِ
(an-Naas:1)
رَبِّ = mudaf
ٱلنَّاسِ = mudaf ilaih
4. إِذَا جَآءَ نَصْرُ ٱللَّهِ وَٱلْفَتْحُ
(an-Nasr:1)
نَصْرُ = mudaf
ٱللَّهِ = mudaf ilaihi
5. وَلَا يَحُضُّ عَلَىٰ طَعَامِ ٱلْمِسْكِينِ
(al-ma'un:3)
طَعَامِ = mudaf
ٱلْمِسْكِينِ = mudaf ilaihi
6. فَقَالَ لَهُمْ رَسُولُ ٱللَّهِ نَاقَةَ ٱللَّهِ وَسُقْيَـٰهَا
(ash-shams:13)
رَسُولُ = mudaf
ٱللَّهِ = mudaf ilaihi
نَاقَةَ = mudaf
ٱللَّهِ = mudah ilaihi
سُقْيَا = mudaf
هَا = mudaf ilaihi







No comments:
Post a Comment