The Fundamentals of Arabic Vocabulary: Word Grammatical Categories in Arabic
Before delving into the science of nahwu and sharaf, it is essential to understand the types of words in Arabic.
Type of words in Arabic (أنواع الكلام) | Part of speech in Arabic
As previously mentioned, Arabic words fall into three categories: noun (اِسْمٌ), verb (فِعْلٌ), and particle (حَرْفٌ). Re-read in the following link types of words in Arabic.
I recommend that you read the following lessons to gain a better understanding:
If you have mastered Arabic parts of speech, we can now move on to the next topic: grammatical categories in Arabic words.
Word Grammatical Categories in Arabic
Arabic words are marked for the following grammatical categories:
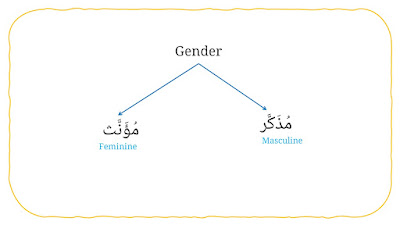
1. Gender
It consists two types, they are:
a. Masculine (مُذَكَّر).
Examples:
a1. Masculine noun (اسم مذكّر), such as: زَيْدٌ (Zaid), بَيْتٌ (baytun).
a2. Verb for 3rd person masculine singular (غَائب مفرد مذكّر), such as:
a21. ذَهَبَ زَيْدٌ (Zaid went).
a22. يَذْهَبُ زَيْدٌ إِلَى المَكْتَبِ (Zaid goes to the office).
b. Feminine (مُؤَنَّث).
Examples:
b1. Feminine noun (اسم مؤنّث), such as: فَاطِمَةُ (Fatimah), سَيَّارَةٌ (car).
b2. Verb for 3rd person feminine singular (غَائب مفرد مؤنّث), such as:
b21. ذَهَبَتْ فَاطِمَةُ (Fatimah went).
b22. تَذْهَبُ فَاطِمَةُ إِلَى السُّوقِ (Fatimah goes to the market).
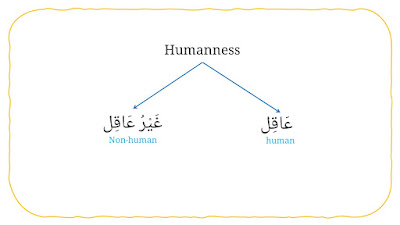
2. Humanness
It consists two types, they are:
a. Human (عَاقِل)
Examples: مُحَمَّدٌ (Muhammad).
b. Non-human (غَيْرُ عَاقِل)
Examples: قَلَمٌ (pen).
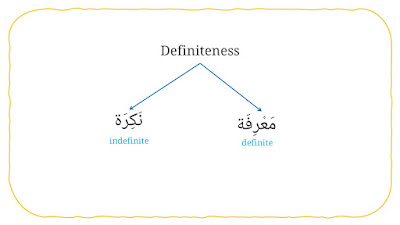
3. Definiteness
It consists two types, they are:
a. Definite (مَعْرِفَة).
Examples: عُمَرُ (Umar), الْكِتَابُ (the book).
b. Indefinite (نَكِرَة).
Examples: كِتَابٌ (a book).
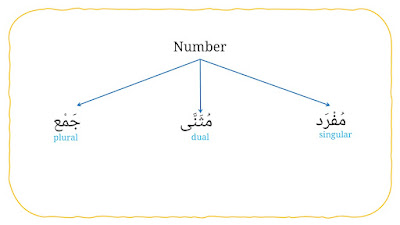
4. Number
It consists three types, they are:
a. Singular (مُفْرَد).
Example: بَيْتٌ (a house).
b. Dual (مُثَنَّى).
Example: بَيْتَانِ (two houses).
c. Plural (جَمْع).
Example: بُيُوتٌ (houses).
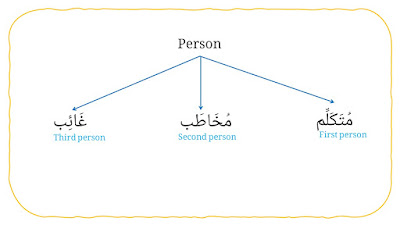
5. Person (for pronoun).
It consists three types, they are:
a. First person (مُتَكَلِّم).
Examples: أَنَا (I), نَحْنُ (we).
b. Second person (مُخَاطَب).
Examples: أَنْتَ (you), أَنْتُمَا (both of you).
c. Third person (غَائِب).
Examples: هُوَ (he), هِيَ (she).
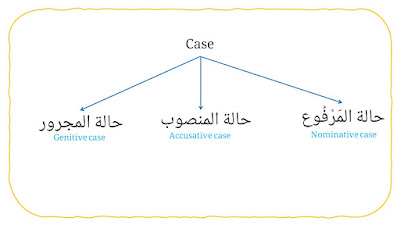
6. Case
It consists three types, they are:
a. Nominative case (حالة المَرْفُوع).
b. Accusative case (حالة المنصوب).
c. Genitive case (حالة المجرور).
You can re-study here: noun cases
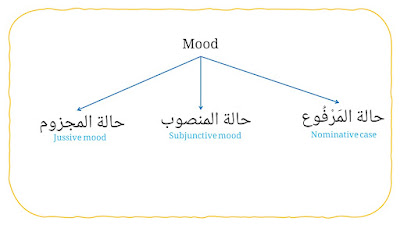
7. Mood (for imperfect verb / فعل المضارع)
It consists three types, they are:
a. Indicative mood (حالة المَرْفُوع).
b. Subjunctive mood (حالة المنصوب).
c. Jussive mood (حالة المجزوم).
We'll learn these moods later, in shaa Allah.
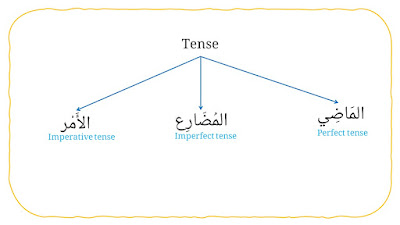
8. Tense
It consists three types, they are:
a. Perfect tense (المَاضِي).
Example: كَتَبَ (wrote).
b. Imperfect tense (المُضَارِع).
Example: يَكْتُبُ (write).
c. Imperative tense (الأَمْر).
Example: اُكْتُبْ (write!).
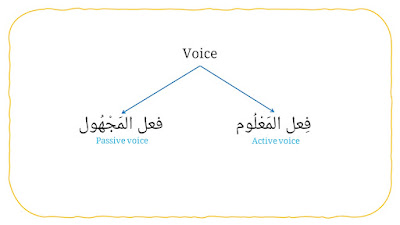
9. Voice (for verb / فِعْل)
It consists two types, they are:
a. Active voice (فِعل المَعْلُوم).
Example: قَرَأَ الكِتَابَ (He read the book).
b. Passive voice (فعل المَجْهُول).
Example: قُرِأَ الكِتَابُ (The book was read).
Summary
1. In Arabic, meaning and grammatical categories are encapsulated in a word.
Examples:
a. بَيْتٌ
a1. Meaning: a house.
a2. Grammatical categories: non-human noun, masculine, singular, indefinite, nominative case.
b. هُمْ
b1. Meaning: they.
b2. Grammatical categories: 3rd person, masculine, plural.
c. ذَهَبَتْ
c1. Meaning: she went.
c2. Grammatical categories: perfect tense for 3rd person feminine singular, indicative mood, active voice.
2. Words and their characteristics:
a. Nouns: gender, number, case, definiteness.
b. Pronouns: person, gender, number, case.
c. Verbs: tense, person, gender, number, voice, mood.


No comments:
Post a Comment