Understanding the Basic Elements of Arabic Grammar: A Guide to Nouns, Verbs, and Particles
Arabic, a rich and complex language, is the key to unlocking a vast cultural and historical heritage.
For students embarking on the journey of learning Arabic, grasping the fundamental building blocks of the language —nouns, verbs, and particles— is essential.
These elements are the foundation upon which sentences are constructed and meaning is conveyed.
By mastering these basics, students will not only improve their ability to communicate effectively but will also develop a deeper understanding of the syntactic beauty of the complex Arabic language.
This guide aims to provide a clear and concise introduction to these critical grammatical components, paving the way for a more comprehensive understanding and fluent use of the Arabic language.
With this basic knowledge, let's delve into the heart of Arabic grammar: the role and variety of nouns, verbs, and particles, which together form the clear expressions in this beautiful language.
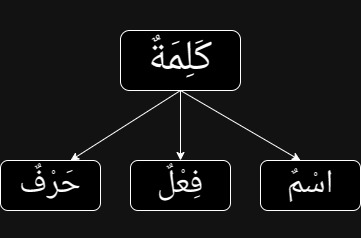
كَلِمَةٌ (a word)
كَلِمَةٌ (kalimatun) is a word that has a meaning.
There are three types of كَلِمَةٌ, they are:
1. اسْمٌ (ismun or ism).
اسْمٌ is a noun. (Read the definition of ism/noun in Arabic).
2. فِعْلٌ (fi'l).
فِعْلٌ is a verb.
3. حَرْفٌ (harfun or harf).
حَرْفٌ is a particle.
اسم (noun)
Ism is a word that has a meaning and does not have any tense (it is not related to the time like present, past, etc.).
Examples:
كِتَابٌ (kitaabun): a book.
قَلَمٌ (qalamun): a pen.
أَحْمَدٌ (Ahmad).
فعل (verb)
fi'l is a word that indicates some action and it relates to the tense or time like present, past, or future.
Examples:
دَرَسَ (darasa): studied.
يَدْرُسُ (yadrusu): study.
حَرْفٌ (harf)
Harf is a word whose meaning can not be understood without another word (ism or fi'l).
Examples:
مِنْ (min), عَلَى ('ala), فِي (fi), etc.
Let's dig deeper into these particles.
Let's take the example of مِنْ (min).
There are many meanings of مِنْ, for example: of/from ... (which relates to time), of/from ... (which relates to place), and so on.
We don't know the true meaning if the particle isn't with a noun or verb. We'll know it if it's accompanied by another word.
For example:
سِرْتُ مِنَ المَدِيْنَةِ: I walked from the city.
In this sentence, مِنْ means “from”.
وَقَعَ هَذَا مِنْ أَلْفِ عَامٍ: This happened since a thousand years.
In this sentence, مِنْ means “since”.
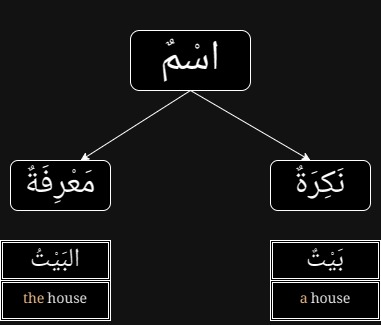
The types of اسم (noun) in terms of definiteness
There are two types, they are:
1. مَعْرِفَةٌ (ma'rifatun or ma'rifah).
مَعْرِفَةٌ is definite.
A definite noun (اسم معرفة) refers to a definite or specific or particular thing.
Examples:
a. Name of the particular person: زَيْدٌ (Zaid).
b. Name of the particular city: مَكَّة (Makkah).
c. Refer to the particular person: المُدَرِّسُ (the teacher).
2. نَكِرَةٌ (nakiratun or nakirah).
نكرة is an indefinite noun. It refers to a general thing.
Examples:
a. Refer to any person: مُدَرِّسٌ (a teacher).
b. Refer to anything: بَيْتٌ (a house).
Study more here: Definite and indefinite noun in Arabic, Nouns in Arabic.
Tanwiin and the definite article
The tanwin (تَنْوِيْن)
The tanwin (تَنْوِيْن) is commonly attached to the end letter of a word that is indefinite (اسم نكرة).
It is translated as "a/an" in English, for example, تُفَّاحٌ (an apple), رَجُلٌ (a man).
Exception: a proper nouns (اسم العلم) such as مُحَمَّدٌ, زَيْدٌ, etc. have tanwin. But, they are definite nouns (اسم معرفة).
A proper noun is one of the nouns that is classified as a definite noun. Notice the “Types of nouns that are classified as definite nouns” section below.
The definite article (اَلْ)
It is known as lam ta'rif (لام التّعرف).
When the definite article "ال" is prefixed to an indefinite word, the indefinite word becomes definite.
Note: When "ال" is prefixed to an indefinite word, the tanwin falls off.
Observe the following example:
رَجُلٌ (rajulun): a man.
الرَّجُلُ (ar-rajulu): the man.
Recap
بَيْتٌ (baytun).
It ends with tanwiin.
It translates to "a house".
It is indefinite noun (اسم نكرة).
البَيْتُ (al-baytu).
It has no tanwiin.
It translates to "the house".
It is a definite noun (اسم معرفة).
Types of nouns that are classified as definite nouns
اسم (noun) that are included in اسم معرفة (definite noun):
1. اسْمُ العَلَمِ (ism 'alam).
Ism 'alam is a proper noun.
Examples: زَيْدٌ (Zaid), أَحْمَدُ (Ahmad).
2. اِسْمُ الضَّمِيرِ (ism damir).
Ism damir is a pronoun.
Examples: هُوَ (he), هِيَ (she).
3. اِسمُ الإِشَارَةِ (ism isharah).
Ism isharah is a demonstrative pronoun.
Examples: هَذَا (this), ذَلِكَ (that).
4. الاِسْمُ المَوْصُلُ (ism mawsul).
Ism mawsool is a relative pronoun.
Example: الَّذِي (that, who).
5. المُنَادَى (al-munada).
al-munada is a called noun (addressee).
al-munada is a vocative case, it is preceded with a vocative particle "يَا".
Example: يَا وَلَدُ (O boy!), يَا زَيْدُ (O Zaid!).
6. المُعَرَّفُ بِاللَّامِ (al-mu'arraf bi al-lam).
A noun that becomes definite because of the definite particle "ال".
Examples: القَلَمُ (the pen), الكِتَابُ (the book).
7. المُضَافُ (al-mudaf).
A noun that is in idafah construction (related to any definite noun).
Examples:
a. كِتَابُ زَيْدٍ (kitaabu zaidin).
In this construction, كِتَابُ is mudaf, whereas زَيْدٍ is mudaf ilaih.
كِتَابُ زَيْدٍ means Zaid's book or the book of Zaid.
In this case, كِتَابُ is a definite noun (اسم معرفة) because it is mudaf.
Exercises
1. Memorize these words:
a. نَجْمٌ: star
b. شَمْسٌ: sun
c. قَمَرٌ: moon
d. سَحَابٌ: cloud
e. سَمَاءٌ: sky
f. أَرْضٌ: earth
g. وَ : and
2. Choose the correct one.
a. Determine the correct form of the word for 'the star'
a1. النَّجْمٌ
a2. النَّجْمُ
a3. نَجْمُ
b. Determine the correct form of the word for 'a moon'
b1. قَمَرُ
b2. قَمَرٌ
b3. القَمَرُ
3. Translate these words into Arabic:
a. The moon:
b. A star:
c. The sun and the moon:
d. The sky:
4. Translate these words into English:
a. النَّجْمُ وَالقَمَرُ:
b. سَمَاءٌ:
c. الأَرْضُ:
Key Answer
The star: النَّجْمُ (an-najmu).
A moon: قَمَرٌ (qamarun).
The moon: القَمَرُ (al-qamaru).
A star: نَجْمٌ (najmun).
The sun and the moon: الشَّمْسُ وَالقَمَرُ
The sky: السَّمَاءُ
النَّجْمُ وَالقَمَرُ: the star and the moon
سَمَاءٌ: sky
الأَرْضُ: the earth


No comments:
Post a Comment