Understanding the Nominative, Accusative, and Genitive Cases of al-Asmaa Al-Khamsah
The previous lesson mentioned al-asmaa al-khamsah (الأسماء الخمسة). I've explained the indication of al-asmaa al-khamsah when they are in nominative case.
Today, I'll delve into al-asmaa' al-khamsah. I'll show you some examples of how members of al-asmaa-ul khamsah group (the five nouns) change their endings when they are in different cases including sentence examples.
What is al-asmaa' al-khamsah?
Al-asmaa' al-khamsah are five special nouns that have unique way of changing their endings according to their grammatical function or their position in a sentence.
What are they?
1. أَبٌ (father).
2. أَخٌ (brother).
3. حَمٌ (brother-in-law).
4. فَمٌ (mouth).
5. ذُو (a word that show "possessor" meaning).
What are the requirements for the five nouns that can be called al-asmaa' al-khamsah?
The five nouns above can be called al-asmaa-ul khamsah, if they have the following conditions:
1. The nouns are singular (مفرد).
If they are in plural form, they are not al-asmaa' al-khamsah.
Example:
أب is singular form.
The plural form of أب is أَبَاءٌ .
So, أَبَاءٌ is not al-asmaa-ul khamsah.
2. The nouns are in annexation (إضافة) form or in genitive construction.
أَبٌ can't be called al-asmaa' al-khamsah.
But, if it join to another word (إضافة), it can be called al-asmaa-ul khamsah.
Example:
أَبُوكَ (your father).
It is idafah form.
أَبُو is mudaf, whereas كَ is mudaf ilaih.
So, you can say it al-asmaa' al-khamsah because it is in idafah condition/form.
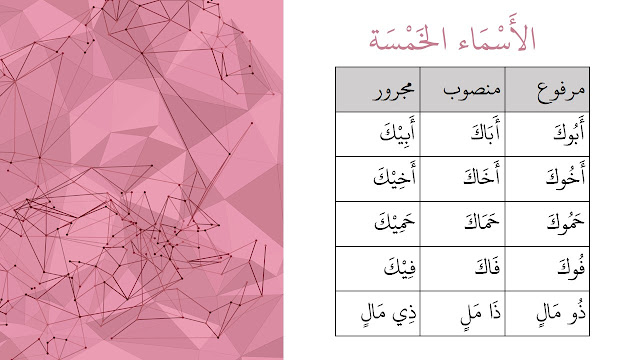
Recap: The examples of asmaa-ul khamsah based on the requirements above.
The asmaa-ul khamsah list (with damir "كَ", and mudaf ilaih "مَالٍ").
1. أَبُوكَ
2. أَخُوكَ
3. حَمُوكَ
4. فُوكَ
5. ذُو مَالٍ
Note: damir "ك" and noun "مَالٍ" as a mudaf ilaih are only example, you can replace them to another word based on context.
After knowing the examples of the five nouns, now we delve into changes in the ending in nominative case, accusative case, and genitive case.
Al-asmaa' al-khamsah and their indication when they are in nominative case, accusative case, and genitive case
The rules:
الأسماء الخمسة تُرْفَعُ بِالوَاو, وَتُنْصَبُ بالألف, وَتُخْفَضُ باليَاء
1. When al-asmaa' al-khamsah are in nominative case (مرفوع), the indication of the raf' condition is al-waw "الواو".
Example:
- أَبُوكَ
- أَخُوكَ
- حَمُوكَ
- فُوكَ
- ذُو مَالٍ
2. When al-asmaa' al-khamsah are in accusative case (منصوب), the indication of the nasb condition is al-alif "الألف".
- أَبَاكَ
- أَخَاكَ
- حَمَاكَ
- فَاكَ
- ذَا مَالٍ
3. When al-asmaa' al-khamsah are in genitive case (مجرور), the indication of the jar/khafd condition is "al-yaa"الياء".
- أَبِيْكَ
- أَخِيْكَ
- حَمِيْكَ
- فِيْكَ
- ذِي مَالٍ
Sentence examples using al-asmaa' al-khamsah in nominative case, accusative case, and genitive case
1. al-asmaa-ul khamsah in nominative case (مرفوع) sentence example.
- أَمَرَ أَبُوهُ وَلَدَهُ (amara abuuhu waladahu).
The meaning: His father commanded his son.
-- أَمَرَ: fi'l madi.
-- أَبُو: fa'il marfuu' (فاعل مرفوع), the indication of the raf' condition is al-waw "و".
أَبُو is also functioned as mudaf.
هُ is mudaf ilaih.
-- وَلَدَ: maf'ul bih mansuub, the indication of the nasb condition is fat-hah "a".
وَلَدَ is also acted as mudaf.
هُ is mudaf ilaih.
2. al-asmaa' al-khamsah in accusative case (منصوب) sentence example.
- أَطِعْ أَخَاكَ (ati' akhaaka).
The meaning: Obey your brother!
-- أَطِعْ: fi'l amr.
-- أَخَا: maf'uul bih mansuub (مفعول به منصوب), the indication of the nasb is al-alif "ا".
أَخَا is also mudaf, and كَ is mudaf ilaih.
3. al-asmaa' al-khamsah in genitive case (مجرور) sentence example.
- اسْتَمِعْ إِلَى أَبِيْكَ (istami' ilaa abiika).
The meaning: Listen to your father.
-- اسْتَمِعْ: fi'l amr.
-- إِلَى: harf jar.
-- أَبِيْ: ism majruur, because it's preceded by harf jar إلَى, the indication of the jar condition is al-yaa "ي"
Summary
After studying al-asmaaul khamsah, you should be able to answer the questions: What is al-asmaaul khamsah, what nouns are included in al-asmaaul khamsah, and what are the conditions for them to be considered al-asmaaul khamsah.
Various changes in the endings in these nouns are observed based on whether they are in nominative, accusative, or genitive cases.
Next lesson
After studying al-marfuu'aat including the sign of marfuu', then I'll explain you accusative case and the signs of it.


No comments:
Post a Comment